Value Added Tax (VAT) in Indonesia (Pajak Pertambahan Nilai, PPN). General regulation, tax rates, calculation and financial reporting.
Value added tax serves is a primary source of budget revenue in most countries worldwide. It was first introduced in France in 1958. Currently, 137 countries enforce VAT, and Indonesia is no exception. This article outlines the key regulations of Indonesian tax law concerning VAT accounting and provides some insights into the general theory of this tax.
Value-added tax, or VAT, is an indirect tax. It is calculated by the seller when goods (work, services, property rights) are sold to the buyer. The seller, in addition to the price of the goods sold, includes the amount of VAT calculated at the established tax rate.
Tax rates and tax base
The VAT rate in Indonesia is 11% as of April 1, 2022, and will increase to 12% by January 1, 2025. Previously, it was 10%.
VAT is calculated by applying the VAT rate to the relevant tax base. In most cases, the tax base is the transaction value agreed upon between the parties involved. By law, all goods and services, unless otherwise stated, are considered taxable. However, there is a list of goods and services that are exempt from taxation.
Non-taxable goods
food and drinks served in hotels, restaurants, or for takeaway and delivery, including food and drinks delivered by caterers, as they are subject to regional tax;
money, gold bars for government foreign exchange transactions and securities.
Tax-free services
religious services;
public services provided by the government to carry out national issues that cannot be provided by other types of business;
services of hotels, catering establishments, art institutions, as well as entertainment establishments, which are subject to regional tax.
VAT financial reporting
Companies and individuals are required to report their business activities and fulfill their VAT obligations on a monthly basis. This means that the tax reporting period lasts for one month. If a company has different divisions, each one must report separately for its registered branches.
An organization can centralize its reporting by submitting a written notification to the tax office, but this is not allowed for all types of companies.

VAT calculation
VAT calculation involves two main components: input VAT and output VAT.
When your organization sells a product or service to a buyer, you set a certain price for it and add the amount of VAT on top, which is then paid to the budget. This amount is classified as output VAT for your organization.
Simultaneously, you purchase goods or services for the operational activities of your organization. The purchase price will also include VAT, which is considered input VAT for you. When filing a tax return, you subtract the input VAT from output and pay the difference to the budget.
For example, you have priced your product or service at 100 rupees, which is the amount you want to earn, but you need to pay tax to the government. You add 11% VAT on top, and the final cost of your service for the buyer becomes 111 rupees, of which the tax amount will be 11 rupees. Your buyer pays these 11 rupees, so the tax is called indirect; you simply transfer it to the budget and reflect it in your reporting. During the month, you provided 5 services, which means the total amount of VAT to be paid to the budget will be: 11 rupees * 5 = 55 rupees.
At the same time, you purchased goods worth 333 rupees, of which 33 rupees was VAT (you will find this information on the invoice provided to you). Your supplier also remits this tax to the budget. The government does not impose double taxation on the same goods, so you can deduct 33 rupees from your tax.
Accordingly, this month, the amount of tax to be paid will be: 55-33 = 22 rupees.
The document reflecting the amount of VAT is called an invoice. Your accountant must issue an outgoing invoice to the buyer and receive an incoming invoice from the supplier. Based on these documents, you will prepare financial statements.
Tax authorities scrutinize incoming invoices; this is the most common type of tax audit, as it constitutes a significant portion of budget revenue. If there are any errors in the documents you receive (for instance, if the address of your company is incorrectly stated), this can lead the tax office to deny the deduction, regardless of whether the error was your fault. You might be required to provide a corrected document within a short period of time, or it may not be considered. This could result in a tax recalculation, an additional payment of the difference to the budget, a revision of the tax return, and potentially a fine (which will be at the discretion of the tax inspector).
Invoices are also examined to ensure that the deducted VAT is related to expenses essential for the organization’s activities, among other aspects. In return, you must issue the correct invoice to the buyer, otherwise your client may encounter similar issues. To accomplish this, you will need to review all documents and maintain communications with your clients’ accounting department. If you find yourself short on time or are not prepared to hire a full-time accountant, you can delegate these responsibilities to an accounting service firm.
Legal Indondesia professionally provides accounting and tax support to organizations, including communication with fiscal authorities, as well as providing advice on taxation.
Invoice
The invoice must contain the following information:
Name, address and tax number (NTN) of the taxpayer;
The name, address and identification number of the buyer;
Type of goods or services, quantity, sales volume, price and discounts;
VAT, which is calculated and highlighted as a separate line;
Code, serial number and invoice date;
The name and signature of the authorized person who signed it.
Organizations prepare documents electronically (electronic Faktur Pajak/e-FP).
Sample invoice (the old tax rate until 2022 is 10%, now it is 11%):
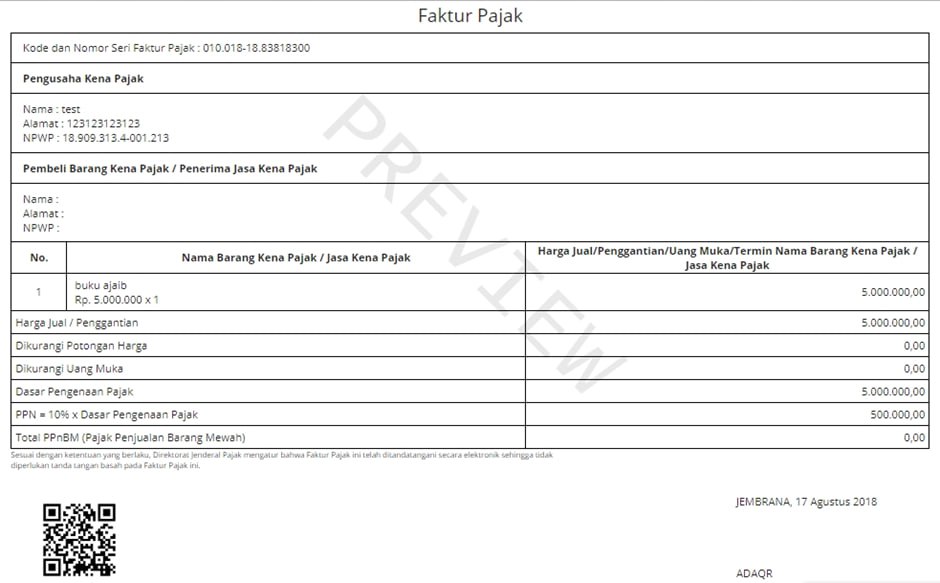
VAT refund
An application for a VAT refund can be submitted at the end of the reporting year. The tax office makes a decision on VAT refund based on an audit for 12 months of the reporting year.
To receive a VAT refund, you must have the appropriate documents and submit them to the tax office within one month from the date of filing the refund application.
VAT on imports
The standardized tariff at the customs or import zone for taxable goods is 11 percent.
Considering economic factors and the heightened requirements for financing the development of the customs sector, the VAT rate can also vary between 5 and 15 percent.
The VAT paid on imports can be offset against the output tax in the tax period during which the payment was made, but no later than 3 months after the end of the respective tax period.
VAT on export
When exporting taxable tangible and intangible goods and services, a 0% tax rate is applied. Please note that specific restrictions may apply to the zero rate.
VAT on strategic goods and services
For the supply or import of strategic goods and services, VAT benefits are provided in the form of tax exemption.
These VAT benefits are applicable for the following purposes:
Stimulating exports and industrial sales in national interests;
Ensuring the possibility of bilateral trade and investment agreements ratified by an international convention;
Promoting the improvement of public health through procurement of vaccines as part of the national vaccination program;
Enhancing the education of the nation by providing general education and religious textbooks at affordable prices to the population;
Encouraging the construction of places of worship;
Implementation of government projects financed by grants and/or foreign loans;
Taking into account international customs rules for certain taxable goods that are exempt from import duty;
Ensuring accessibility to taxable goods/services necessary for disaster management;
Ensuring the availability of public air transport to improve the flow of goods and people in areas where other transport is not available;
Supporting the availability of certain strategic goods and services in the context of national development, including:
essential products for the population;
certain medical services and services within the system of national health insurance programs;
non-profit social services;
financial services;
insurance services;
educational services;
public transport services on land and water, as well as domestic air transportation services, which are an integral part of foreign transportation services;
employment services.
Additional tax base
In certain cases, the VAT tax base includes the following items:
the market value of transactions between related parties, remaining inventories of taxable goods upon liquidation of a company and the sale of assets not originally intended for sale;
the cost of sales (selling price minus gross profit) for goods used for internal purposes or given as gratuitous gifts, as well as internal supplies of goods (for example, between branches or from head office to branches);
the auction price of supplies of taxable goods conducted through an auction employee;
the agree-upon price for supplies of taxable goods through an intermediary trader;
the average result per movie for theatrical distribution;
IDR 12 million per copy for imported movies;
20% of the total amount of expenses incurred or paid, excluding the cost of acquiring land for self-construction of a building;
retail selling prices for the delivery or import of tobacco products
10% of the actual invoice for parcel delivery services
10% of the actual invoice amount for travel agency services, the supply of which is not based on commission;
20% of the selling price for supplies of gold jewelry, including services performed by the factory producing gold jewelry;
10% of the actual invoice amount for the delivery of freight forwarding services, which include freight.














